What is female urology?
Urology is a field of medicine focussing on diseases of the urinary tract system, which includes include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. Female and reconstructive urology is a sub-specialty of urology that treats and assesses patients with urinary incontinence, urological diseases and the reconstruction of the urinary tract.
Female urology is a subdivision of this sub-specialty and it covers a group of conditions that are experienced by women, such as urinary incontinence, overactive bladder and pelvic organ prolapse. A female urologist specialises in the treatment of these diseases and has a thorough knowledge of the female pelvic floor. They can also treat urological conditions which affect both sexes, including urinary tract infections (UTI), cystitis, kidney stones, kidney cancer and bladder cancer.
What conditions are treated within female urology?
Conditions commonly treated within female urology include:
- Urinary incontinence
- Overactive bladder
- Pelvic prolapse
- Pelvic floor problems
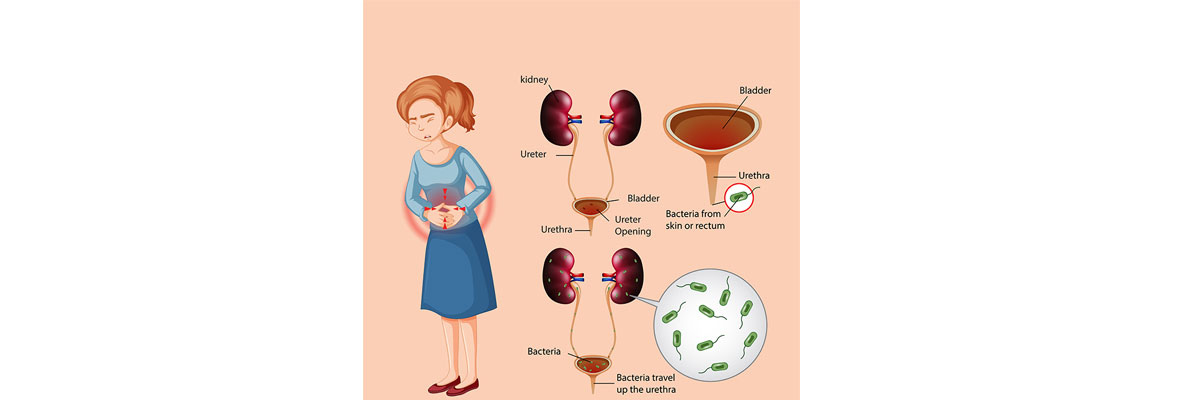
- Urinary tract infections
- Cystitis
- Kidney stones
- Kidney cancer
- Bladder cancer
When should you see a urologist?
Women should see a urologist who specialises in female urological problems if they experience any of the following symptoms:
- Blood in their urine
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Cloudy urine
- A frequent urge to urinate
- Pain or a burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Urinary leakage
Talking about female urological problems may be uncomfortable, but acknowledgement is the first step towards treatment and permanent solutions. Many women may not know how common urological issues are and the fact that they are treatable. This prevents them from talking about the issue and seeking proper care or medical assistance. We are here to change that for you.
There are various urological problems that both men and women face. We will talk about some of the most common female urological problems and how treatment can help relieve pain or discomfort.
Postpartum Urinary Incontinence:
This refers to the very common condition that new mothers face - involuntary leakage of urine. This is often found to occur when there is sudden pressure on the abdominal muscles - laughing, sneezing, coughing, jumping, lifting weights or carrying out a strenuous activity. If you are experiencing this, there is no need to panic - it is a very common condition that is treatable. Talk to a urologist to address and treat this issue. There are non-invasive treatments that include physical and behavioural therapies. The extent of this condition varies from woman to woman. If the issue persists or worsens, there are other options such as surgery.